t1 protocol smart card In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4 Organization, security and commands for interchange. [1] The most recent firmware versions for the UltiMaker S5 are 9.0.0 (Latest) and 8.3.1 (Stable): Update your UltiMaker S5 via USB. The UltiMaker S5 was first released in 2018. In March 2020, UltiMaker introduced a new version of the .
0 · The DS8007 and Smart Card Interface Fundamentals
1 · Smart Card Reader T0 T1 communication on APDU level
Hi Andrew, In the NFCLink Standalone Getting Started Guide, it has below note about NFC communication with Android phones for read/write.. For P2P operation, can you try .
The DS8007 and Smart Card Interface Fundamentals
I am struggle to understand what protocol I have to use to communicate with the card T0 or T1? So, correct me if I am wrong, but the reader actually decides by itself what protocol to use to communicate with the card if the card supports both.
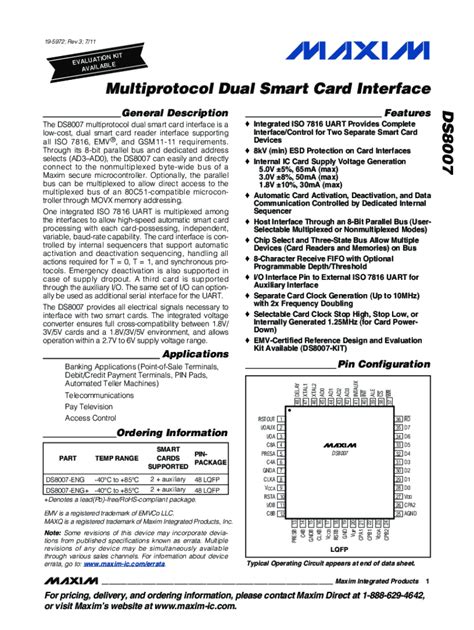
The DS8007 is a multiprotocol, low-cost, dual, smart card interface that supports .
I am struggle to understand what protocol I have to use to communicate with the card T0 or T1? So, correct me if I am wrong, but the reader actually decides by itself what protocol to use to communicate with the card if the card supports both. The DS8007 is a multiprotocol, low-cost, dual, smart card interface that supports all ISO 7816, EMV™, and GSM11-11 requirements. This one mixed-signal peripheral manages all the details of the interface between a microcontroller and two, independent smart cards.
In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4 Organization, security and commands for interchange. [1] I have also an ACR38 smart card reader that it support both T=0 and T=1 protocols. (I have T=0 communication with one card successfully and T=1 communication with this card successfully.) I wrote the below program and upload it on the card to send and receive extended APDUs: private ExAPDU() {.The ISO 7816 standard defines the necessary protocols to communicate with a smart card. Although the communication software is tested with TimeCOS, the basic communication protocol (ISO 7816, T = 0) implemented in this application note is common with all smart cards. 2012 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.The TA1, TB1, TC1, and TB2 characters are referred to as the global interface bytes and are fundamental to the operation of the card. TA1 defines the basic characters of the serial transmission, FI is the clock rate conversion factor and DI is the bit rate adjustment factor.
Smart Card Reader T0 T1 communication on APDU level
This paper introduces the SmartLogic, which is a smart card research tool that can be used in different modes such as eavesdropping, card emulation, man-in-the-middle attacks (or so-called “wedge” attacks) and relaying. We demonstrate the capabilities of .The Smart Card library for PIC microcontrollers support ISO 7816-3 and ISO 7816-4 standard protocols. It allows the PIC microcontroller to communicate with smart cards compatible with these protocols. The library supports both T=0 and T=1 smart card protocols.The Smart Card library for PIC microcontrollers support ISO 7816-3 and ISO 7816-4 standard protocols. It allows the PIC microcontroller to communicate with smart cards compatible with these protocols. The library supports both T=0 and T=1 smart card protocols.
ISO7816-3 specifies communication protocol between smart card and reader on the level of the electrical signals. • Protocol T=0 – byte-oriented protocol. Older than T1, designed for maximal simplicity and minimal memory requirements. Error detection only .I am struggle to understand what protocol I have to use to communicate with the card T0 or T1? So, correct me if I am wrong, but the reader actually decides by itself what protocol to use to communicate with the card if the card supports both. The DS8007 is a multiprotocol, low-cost, dual, smart card interface that supports all ISO 7816, EMV™, and GSM11-11 requirements. This one mixed-signal peripheral manages all the details of the interface between a microcontroller and two, independent smart cards.
In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4 Organization, security and commands for interchange. [1]
I have also an ACR38 smart card reader that it support both T=0 and T=1 protocols. (I have T=0 communication with one card successfully and T=1 communication with this card successfully.) I wrote the below program and upload it on the card to send and receive extended APDUs: private ExAPDU() {.The ISO 7816 standard defines the necessary protocols to communicate with a smart card. Although the communication software is tested with TimeCOS, the basic communication protocol (ISO 7816, T = 0) implemented in this application note is common with all smart cards. 2012 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.The TA1, TB1, TC1, and TB2 characters are referred to as the global interface bytes and are fundamental to the operation of the card. TA1 defines the basic characters of the serial transmission, FI is the clock rate conversion factor and DI is the bit rate adjustment factor.
This paper introduces the SmartLogic, which is a smart card research tool that can be used in different modes such as eavesdropping, card emulation, man-in-the-middle attacks (or so-called “wedge” attacks) and relaying. We demonstrate the capabilities of .The Smart Card library for PIC microcontrollers support ISO 7816-3 and ISO 7816-4 standard protocols. It allows the PIC microcontroller to communicate with smart cards compatible with these protocols. The library supports both T=0 and T=1 smart card protocols.
The Smart Card library for PIC microcontrollers support ISO 7816-3 and ISO 7816-4 standard protocols. It allows the PIC microcontroller to communicate with smart cards compatible with these protocols. The library supports both T=0 and T=1 smart card protocols.
program smart card windows
Reading NFC Tags with Android (Kotlin) Near Field Communication (NFC) Tags are used to store Data such as URLs, Contact information or even simple text. Mobile devices that support NFC Technology have the capability .
t1 protocol smart card|The DS8007 and Smart Card Interface Fundamentals